Indigo Blockchain Resource Center
The potential of blockchain in the energy and utilities industry could be transformative. Over the past 12 months we have seen a host of utilities engage with the technology and launch pilots across the world. As part of our emerging technologies offering, Indigo has created a dedicated resource center for the application of blockchain technology in the energy and utilities industry. Here you will find global activities, emerging use cases and startups that are deploying the technology. The resource center will be consistently updated with new developments. Contact us to find out how we help utilities navigate this new space.
Report: Blockchain – U.S. and European Utility Insights
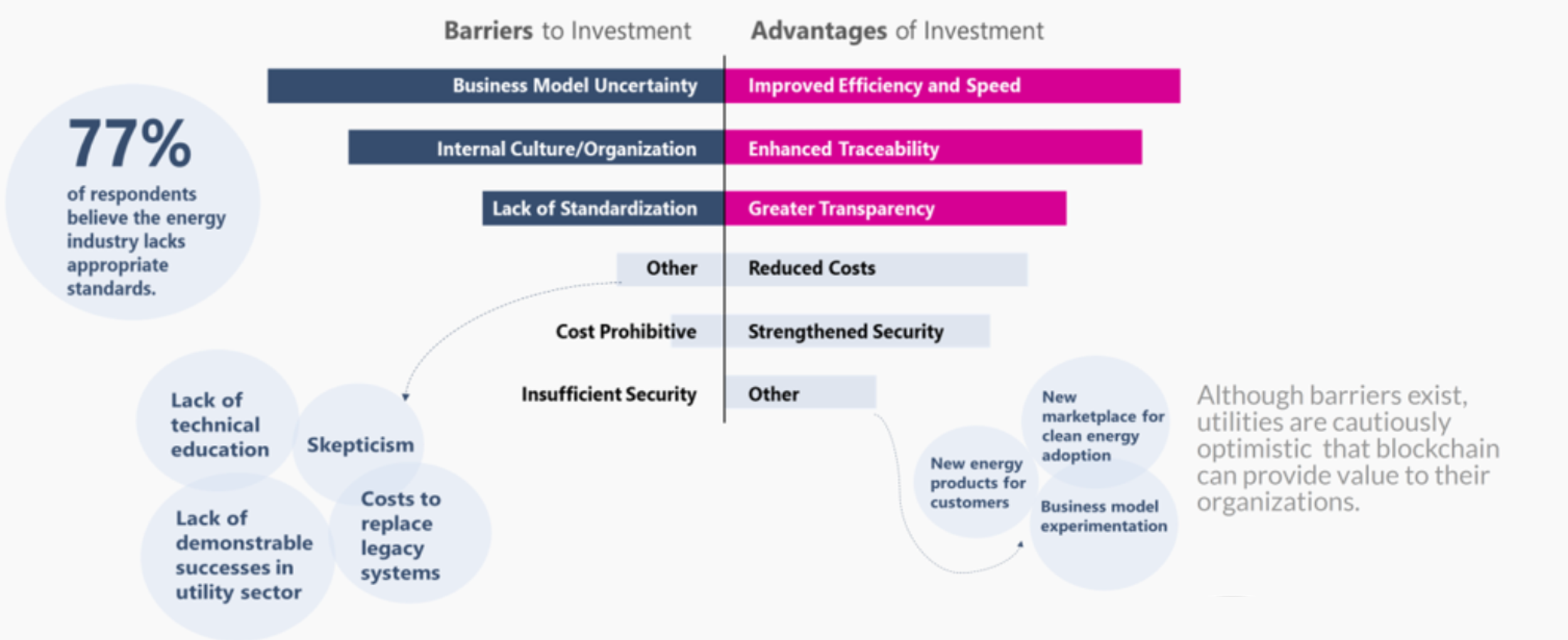
Indigo authored a report for the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) that features results and insights from a survey we conducted of 15 utilities and one regional transmission operator (RTO) across the US and Europe. Although 70% of respondents believe the utility blockchain market is still emerging, there is a great deal of activity in the space with several utilities conducting pilots, developing proof of concepts, and encouraging internal research. As we enter a more mature phase of understanding of the technology in the energy and utilities sector this report serves as a “temperature gauge” of adoption. Read more here.
Utilities surveyed included: Burlington Electric Department, Centrica, Con Edison, DTE Energy, EDF, Enel, EON Climate and Renewables, Exelon, Hawaiian Electric, National Grid Partners, New York Power Authority, Pacific Gas & Electric, Southern Company, Tennessee Valley Authority and Tuscon Electric Power.
Global Blockchain Activity - Interactive Map
In this interactive map, Indigo tracks the global adoption of blockchain in the energy and utilities industry. Across the value chain, the possibilities of leveraging the technology are vast and as such activity is moving quickly. To that end, we will update this map with pilot news, startup launches and other notable activity. If you are on a mobile device - tilt your screen horizontally to view.
“Like the Internet, blockchain is an open, global infrastructure upon which other technologies and applications can be built. And like the Internet, it allows people to bypass traditional intermediaries in their dealings with each other, thereby lowering or even eliminating transaction costs”
EMERGING ENERGY BLOCKCHAIN USE CASES
While it is still early days for blockchain and while pilots at this stage are contained, the possibilities of leveraging P2P technology where both computers and people share a distributed ledger are vast. In the future, networks of blockchains may interact over time to fundamentally change the market. In the graphic above we highlight where the major activity is occurring in the industry right now from a use case perspective. Currently over 100 use cases of the technology have been identified in the energy industry. Indigo is consistently compiling and evolving a list of potential blockchain applications for the sector in our 'energy blockchain use case repository'. These use cases are based on our recent requirements analysis work and the unique characteristics of a utilities' operating environment. For some high-level information on use case categories see here.
Industry Sentiment - The View from Energy Executives
In our research for the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) we featured results and insights from a survey of 15 utilities and one regional transmission operator (RTO) across the US and Europe that identified a series of challenges. Although 70% of respondents believe the utility blockchain market is still emerging, there is a great deal of activity in the space with several utilities conducting pilots, developing proof of concepts, and encouraging internal research. As we enter a more mature phase of understanding of the technology in the energy and utilities sector this report serves as a “temperature gauge” of adoption.
In August 2016, the German Energy Agency GmbH (dena) surveyed 70 German decision-makers and energy executives on their current opinions, actions and visions of blockchain. The results point to a vibrant future for the technology with over 50% of the respondenets either planning or implementing blockchain pilots. Similarly, when asked about their judgment regarding the future of blockchain in the energy sector, 60% see further dissemination likely and over 20% seeing blockchain as a game changer for the energy supply industry.
The Potential Impact on The Utility Business Model
From our initial analysis, blockchain may provide an opportunity to transform some existing utility processes. For example, beyond the much-talked-about applications behind the meter, utilities may be able to leverage this technology for supply chain, asset management and organizational performance applications. In reality, there will be largely three types of impacts of blockchain technology on the utility value chain. Firstly, there will be those areas where there is limited-to-no impact, for other areas the technology may support existing processes and make them even more robust and efficient, for other areas however, we may see some level of disruption. Overall, we have begun to analyze these types of impacts across the utility value chain in this resource center and expect this view to evolve as the technology matures. In the long-term, blockchain has disruptive potential across the utility value chain. In the graphic above we highlight some of the core utility processes that will perhaps be both supported and disrupted by the technology. It is important to point out however, that blockchain will not replace relational databases for business critical processes in the medium term. Indeed, at this stage, relational databases have a decisive advantage when it comes to performance, however, blockchain has an advantage when it comes to providing a robust, fault-tolerant way to store critical data and manage smart contracts.
How the Core Technology is Evolving
Currently there are approximately 40 startups operating globally in the energy blockchain space. These startups are working with the underlying technology of bitcoin and particularly on permissioned (private) platforms. However, the technology still needs time to mature and the core developer network estimates that this may be 2-5 years away, as such, we are in the midst of an experiment and right now blockchain technology is too slow to handle real-time market needs. What is needed is a much higher output volume e.g. 1 million transactions per second, and that needs to be combined with privacy concerns. Unlike the financial services industry, the energy industry needs much faster confirmation times to make IoT applications a reality, and unlike the financial service industry, permissioned based blockchains will emerge due to national, regulatory and privacy concerns. Currently we are seeing the creation of consortia in the industry that are aiming to improve the underlying technology and trial specific use cases, examples of consortia include Enerchain by PONTON.
Stakeholder Activity and Market Taxonomy
Stakeholder Activity and Market Taxonomy
In terms of evolving vendor and utility activity, we are seeing categories of use case activity emerge across the value chain. These can be broadly grouped across, bitcoin bill pay, P2P trading, EV charging and sharing, renewable cryptocurrencies, wholesale trading and settlement and the creation of consortia and energy blockchain labs. In the taxonomy above we have begun to categorize this activity and highlight some of the key stakeholders and vendors across each area, for some high-level information on these use case categories see here.
The Rise of the "ICO" in Energy
ICO Tracker in Energy
At this stage six energy-focused blockchain firms across North America, Europe, Australia and Asia are on pace to exceed $200 million in token sale proceeds by the end of 2017, a review by S&P Global Market Intelligence found. With this in mind, in the above we highlight 15 energy and utility related ICOs that have occurred or will occur in the near term in the industry. The vast majority of energy startups at this stage are focusing on very similar solutions – building decentralized energy marketplaces.
The 4th Industrial Revolution (4IR) & The Role of Energy
The 4th Industrial Revolution (4IR) and the Role of Energy
Over the next decade advancements in Artifical Intelligence (AI), distributed ledgers and robotics will impact a variety of sectors. For utilities, these trends combined with the dramatic changes in the energy transition such as distributed energy resources, increased proliferation of sensors on infrastructure and behind the meter devices and demand management advances will unleash a variety of transformative use cases in the sector. For example, devices which auto-detect demand levels on the grid and reduce power could be powered by AI and recorded by blockchain. For more information on how blockchain will interact with AI and robotics, see here.
How Indigo helps utilities leverage blockchain technology
At Indigo, we help utilities navigate this new domain through executive workshops, use case screening, technology partnership identification and market analysis. Please contact us to find out more. Our approach is focused on launching successful pilots that are defined by conducting robust requirements analysis and ultimately holistic use case screening. For example when selecting use cases, important screening criteria for utilities should include the following considerations:
Both data and process transparency is valuable
Transactions require cryptographic certainty
There is a need for marks of authenticity between participants
Currently multiple parties perform data entry
Participants will benefit from a synchronous processes
There is an opportunity to reduce compliance costs
Although blockchain may provide an opportunity to transform some existing utility processes, the major opportunities in the near term will focus on the changes in the industry, and the handshake between distributed energy resources and utility analytics. That said, while the adoption journey may begin with community P2P markets, transactive home energy management and EV charging settlement, however, over time, we may see parts of the utility value chain impacted with transactive grid settlement, real-time asset valuation and products designed utilizing smart contract functionality. Ultimately, considerations regarding the design of actors and the role of balancing groups and the development of a carbon market with distributed registry may be a reality enabled by blockchain. In this environment, hundreds of market processes both internal and external to a utility would need to be reexamined.
For further insights and research see our latest report and infographic on blockchain in Energy and Utilities.